Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebashi, Katsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Tanaka, Tadao; Araki, Kunio*; Saito, Masao*
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.242 - 247, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-009, 35 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of TRU wastes, nitrogen generation by denitrifying bacteria could provide significant impact on the assessment of this system, because nitrate contained in process concentrated liquid waste might be electron acceptor for denitrifying bacteria. In this study, the activities and tolerance of denitrifying bacteria under disposal condition were investigated. pseudomonas denitrificans as denitrifying bacteria was used. The results showed that Pseudomonas denitrificans had activity under reducing condition, but under high pH condition (PH 9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
Moriyama, Hirotake*
JNC TJ8400 2000-050, 47 Pages, 2000/03
In support of the safety assessment of geologic disposal of high levcl radioactive wastes, the solubility of transuranium elements was studied. The solubility of PuO
 xH
xH O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K
O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K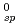 and the stability constant
and the stability constant 
 of Pu(OH)
of Pu(OH) were obtained. The obtained K
were obtained. The obtained K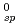 value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO
value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO 3
3  xH
xH O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K
O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K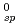 was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ueta, Shinzo*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-069, 41 Pages, 1999/11
As a part of the evaluation for the sorption phenomena of nuclides in compacted bentonite, apparent diffusivities for uranium, neptunium and technetium that are redox-sensitive elements, were measured under reducing conditions. Bentonite used was a sodium bentonite, Kunigel V1. Apparent diffusivities were measured by using in-diffusion method (concentration profile method), under the conditions with varying dry densities of compacted bentonite and sorts of the solution used for water saturation of bentonite in diffusion experiments. As a result of the measurements, following ranges of values for apparent diffusivities were acquired. ...
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu; Arthur, R. C,*
JNC TN8400 99-033, 153 Pages, 1999/07
The results of hydrochemical investigations of groundwaters in the Kurihashi granodiorite at JNC's Kamaishi in-situ tests site indicate that these solutions are: (1)meteoric in origin, (2)chemically reducing (at depths greater than a few hundreds meters), (3)relatively young [residence times in the Kurihashi granodiorite generally less than about 40 years, but groundwaters older than several thousand years BP (before present) are also indicated by preliminary carbon-14 dating of samples obtained from the KH-1 borehole], (4)Ca-HCO type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO
type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO type groundwaters with increasing depth. The evolution of groundwater compositions in the Kurihashi granodiorite is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, AI, carbonate and sulfate) in the Kurihashi granodiorite if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO
type groundwaters with increasing depth. The evolution of groundwater compositions in the Kurihashi granodiorite is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, AI, carbonate and sulfate) in the Kurihashi granodiorite if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10
concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10 bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), microcline (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). Discussions with international experts suggest a systematic approach utilizing reaction-path models of irreversible water-rock interactions in open systems may be needed to more realistically model groundwater evolution at the Kamaishi test site. Detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., fracture mineralogy) may be required to adequately constrain such models, however.
bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), microcline (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). Discussions with international experts suggest a systematic approach utilizing reaction-path models of irreversible water-rock interactions in open systems may be needed to more realistically model groundwater evolution at the Kamaishi test site. Detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., fracture mineralogy) may be required to adequately constrain such models, however.
G M N BASTON*; J A BERRY*; M BROWNSWORD*; D J LLETT*; C M LINKLATER*; S W SWANTON*; Tweed, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 99-078, 72 Pages, 1999/03
A desk study has been carried out to establish the feasibility of measuring the oxidation state of plutonium under near-neutral strongly-reducing conditions. X-ray absorbance spectroscopy appears to be capable of establishing the oxidation state of plutonium sorbed on a suitable substrate. An experimental and modelling investigation has been performed to study the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone under strongly-reducing conditions at three concentrations of carbonate. Appropriate synthetic rock-equilibrated de-ionised water and seawater were used. A model has been developed to describe the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone in de-ionised water and seawater. Predicted R values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-005, 49 Pages, 1997/03
None
*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; *
PNC TJ1058 97-004, 179 Pages, 1997/03
None
Nakayama, Shinichi; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nagano, Tetsushi
JAERI-Conf 97-002, p.13 - 14, 1997/02
no abstracts in English
Chikasui Gijutsu, 36(12), p.4 - 19, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
; Yasunaka, Hideo
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (1), p.36 - 45, 1989/00
no abstracts in English